The Seoul Metropolitan Government (SMG) has pursued the three goals of strengthening the competitiveness of shared businesses, spreading shared benefits, and strengthening networks in accordance with the second phase of the sharing city plan, which has been implemented since 2015.
As a result, 78 sharing companies have been designated and operated as of 2017. The number of members of SOCAR, the sharing car, has grown by a factor of over 30 (from 40,000 to 1.35 million) and Modu (meaning “together”) Company, the parking lot sharing service, has grown by more than 500 times. In order to improve understanding of and interest in the sharing economy, Seoul is carrying out various educational programs such as “Sharing Economy Startup School” in cooperation with 25 local governments and elementary/middle/high schools.
As a result of activities like the ones mentioned above, 98% of respondents answered that they have heard about one or more sharing projects promoted by the SMG in a survey on awareness of sharingpolicies of Seoul (June 2017). In particular, the policy experience and satisfaction of citizens appeared high in the field of public bicycle operation, which has been promoted actively by Seoul since last year. However, the citizens’ overall experience level on the sharing resources scattered by each local autonomous district was below 20%.
In order to improve the citizens’ accessibility to the sharing policies and projects, this year the SMG has been carrying out a project of designating “Sharing Villages”. The purpose of designating “SharingVillages” is to select places where sharing resources are concentrated as a result of the various sharingpolicies promoted by the SMG over the past 4 years, and to support such places by expanding moresharing resources and providing the expenditures necessary for the operation of the sharing resources to help citizens easily access the sharing culture in their everyday lives. In consideration of the social characteristics of Seoul, with its high ratio of large-scale apartment housing complexes, not only the villages, where smaller households are gathered, but also complexes with large numbers of apartments are all included in the designation target of Sharing Villages. In case a complex of apartment houses is designated as a Sharing Village, the idle spaces will be created as sharing places, and the sharingresources will be available to both the residents of the relevant apartment houses and local residents. The SMG will support the expenses necessary for the creation of sharing villages and provide the necessary administrative support in cooperation with the local government. In early July, Seoul designated an area of apartment houses in Seongbuk-gu District as a Sharing Village after a screening process by committee.
In the “Sharing Apartment Houses” in Seongbuk-gu District, designated as a part of a pilot project, various sharing resources, such as shared parking lots, car sharing, public bicycles, and others will be intensively allocated. Residents’ associations will play a leading role in the active creation of sharingvillages. The project to designate sharing villages will be an important trial in testing the possibility of a sharing city, in that various kinds of sharing resources are concentrated in the relatively small area of village units. If the sharing village experiment is completed successfully, the SMG will prepare guidelines and disseminate it to other local governments.
Further, the SMG is searching for new sharing areas to lead to the rapid growth of sharing projects. One of these new areas is the sharing of the rooftops of houses.
I have learned that many activities are carried out on rooftops in other countries. Unfortunately, at the moment it is not easy to share rooftops in Korea. There are various laws and regulations regarding the use of the rooftops. With attention to the citizens’ high desire to use these rooftops, however, the SMG has plans to conduct sharing events with sharing companies by utilizing rooftop parks, which were built in the public area but have not been used. We will do as much as is allowed by the current laws.Seoul is going to hold a total of 20-30 times of events from September to November 15th this year. The SMG expects to improve citizens’ awareness of the rooftop space and to open more rooftop spaces to citizens through these events.
Finally, Seoul is primarily focusing on the project of reorganizing the sharing hub.
An integrated map information service will be introduced as one of the main contents of sharing hub reorganization. The integrated map information service is a service that assists in the provision of the various sharing resources owned by Seoul Metropolitan City, autonomous districts, sharing companies, and sharing groups. A function to search for and display the necessary services based on the user’s current location will be installed in the integrated map information service. In addition, the convenience of accessibility will be improved to help users easily access a variety of sharinginformation. In addition, a function that provides domestic and foreign data together will be reinforced. The reorganized sharing hub will be open to the public early next year. Apart from the restructuring ofsharing hub, we are going to issue a sharing newsletter beginning this August. The SMG will do its best to send you all the news happening in Seoul once a month.
The SMG will continue to make efforts to establish and develop a model for the sharing economy at the city government level. I would like to ask all partner cities of the Alliance to share the successful policies of your cities for the third phase of Sharing Seoul, to be followed after the completion of the second phase of Sharing Seoul in 2018.
Written by Jun Hyo-kwan, Director of the Seoul Innovation Bureau of the Seoul Metropolitan Government (SMG)
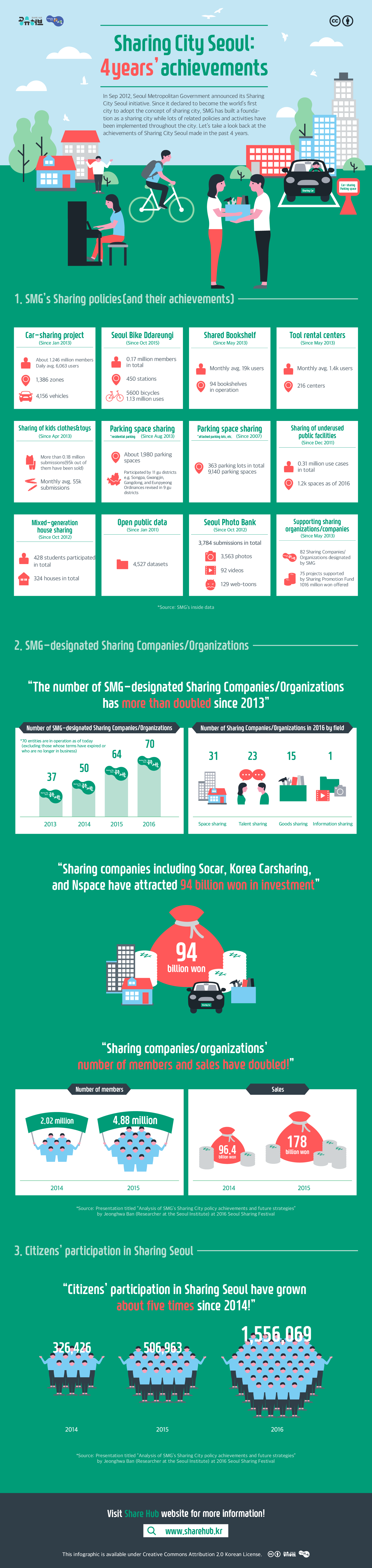
Infographic Sharing City Seoul: 4 years’ achievements, December 27, 2016 by Sharehub